
- Hormone - A hormone is a chemical secreted by an endocrine gland and carried in the bloodstream to target organs where it performs a specific function.
- Functions of Hormones - The varying actions performed by hormones may be fast-acting (e.g. Adrenalin is a hormone that rapidly speeds up the heart and breathing rates when we get a fright), or may be slow-acting (e.g. Human Growth Hormone regulates the many body processes involved in growing from conception to death).
- Endocrine Glands - These glands are ductless, and secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream.
- Examples of Endocrine Glands - adrenal glands, thyroid gland, and ovaries and testes
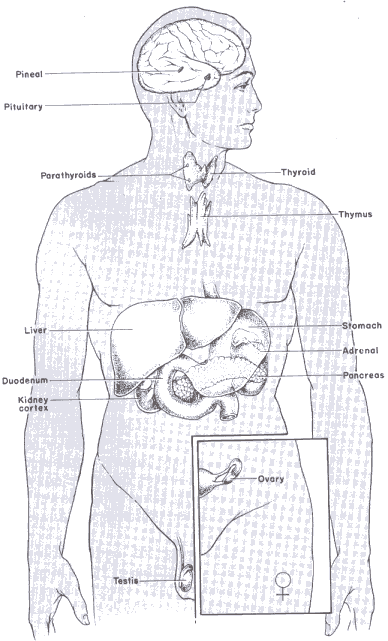
ENDOCRINE |
HORMONE SECRETED |
TARGET ORGAN |
EFFECT ON BODY |
| Pituitary | thyrotrophin |
thyroid | controls secretion of thyroxin |
| corticotrophin | adrenal glands | controls secretion of cortisol | |
| gonadotrophin | gonads | controls secretion of sex hormones | |
| human growth hormone | all cells | promotes body growth | |
| antidiuretic hormone | kidneys | promotes water reabsorption | |
| oxytocin | uterus | contracts uterus | |
| prolactin | breasts | controls breast milk secretion | |
| Thyroid | thyroxine | all cells | controls metabolism |
| Parathyroid | parathyroid hormone | bones, kidneys | increases blood calcium |
| Adrenal | adrenaline ('fight or flight' hormone) |
most cells | controls blood circulation, increases heart rate blood glucose and blood flow |
| cortisol | most cells | controls metabolism of fats carbohydrates and proteins | |
| sex hormones | gonads | development of sex characteristics | |
| Pancreas | insulin | all cells | lowers blood glucose |
| glucagon | all cells | increase blood glucose | |
| Gonads (Testes and Ovaries) | oestrogen | sex organs | female sex characteristics |
| progesterone | sex organs | regulates menstrual cycle | |
| testosterone | sex organs, muscle | male sex characteristics, promotes growth |
HOMEOSTASIS (or BODY BALANCE)
- Homeostasis - This is the tendency to maintain stability or uniformity in an organism's internal environment. A balance is maintained of temperature, and of chemicals such as water, salts and glucose.
- A Stimulus-Response Model
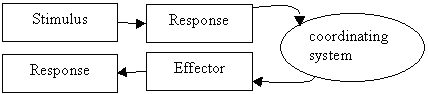
- Maintaining Human Body Temperature (37oC)
- If body temperature rises above 37oC - The skin produces sweat which cools the body by using excess body heat to evaporate it. Also the body can consume cool drinks, find cool shade, radiate heat through the skin or by breathing out warm air, and by defaecation or urination.
- If body temperature falls below 37oC - The muscles may shiver to produce heat through friction, skin muscles may contract to produce insulating air pockets next to the skin with 'goosebumps' and upright hairs, the body consumes warm drinks or finds warm shelter.
- Maintaining Water Balance
- Water is essential to the body for chemical reactions to take place within cells.
- The amount of water consumed in food and drink should equal the amount of water lost through breathing out, sweating, urination and defaecation.
- Maintaining Salt Balance
Excess salt in humans is excreted in both urine and sweat.