
- Excretion - Excretion is the removal of the metabolic wastes of an organism. Wastes that are removed include carbon dioxide, water, salt, urea and uric acid. All excreted wastes travel at some time in the blood.
- Organs of the Excretory System
- Lungs - removal of excess carbon dioxide
- Liver - produces urea and uric acid as a by-product of the breakdown of proteins
- Skin - removal of excess water, salt, urea and uric acid
- Urinary System - kidneys filter the blood to form urine, which is excess water, salt, urea and uric acid
THE SKIN
- 2 Layers of the Skin
- Epidermis - outer protective layer without blood vessels
- Dermis - inner layer containing blood vessels, sensory nerve endings, sweat and oil glands, hairs, and fat cells
- Functions of the Skin
- Excretion - Wastes such as excess water, salt, urea and uric acid are removed from the body in sweat.
- Waterproofing - The skin with its oil glands prevents the entry of water into, and loss of water out of the body.
- Protection from Disease - The intact skin prevents invasion of micro-organisms and dust into the body.
- Protection from Ultraviolet Rays - Pigments reduce the intake of UV rays.
- Regulation of Body Temperature - The thin layer of fat cells in the dermis insulates the body. Contraction of small muscles attached to hairs forms 'goosebumps' and creates an insulating blanket of warm air. Also, sweat produced by sweat glands uses excess body heat to evaporate, providing a cooling effect.
- Sensory Detection - The nerve endings or receptors in the dermis detect heat, cold, touch, pressure and pain.
THE URINARY SYSTEM
Urine
- The first nitrogenous waste to be formed from the breakdown of protein is ammonia, a highly toxic chemical that is quickly converted by the liver to urea and uric acid. These are less toxic than ammonia and are transported in the blood to the kidneys for excretion in urine. Urine consists of excess water, excess salt, urea and uric acid.
Parts of the Urinary System
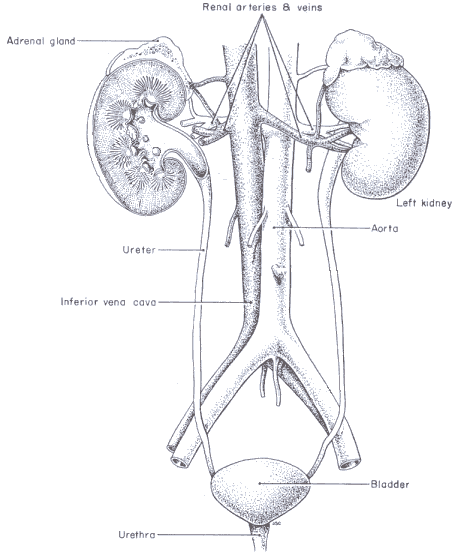
- Renal Arteries - 2 renal arteries constantly transport blood to the kidneys.
- Kidneys - 2 kidneys composed of millions of nephrons constantly filter about 170 to 200 litres of blood to produce about 1.5 to 2 litres of urine daily.
- Renal Veins - 2 renal veins return useful nutrients back into the bloodstream.
- Ureters - 2 ureters carry urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder.
- Urinary Bladder - The urinary bladder temporarily stores urine until it is released from the body.
- Urethra - The urethra is the tube that carries urine from the urinary bladder to the outside of the body. The outer end of the urethra is controlled by a circular muscle called a sphincter.