
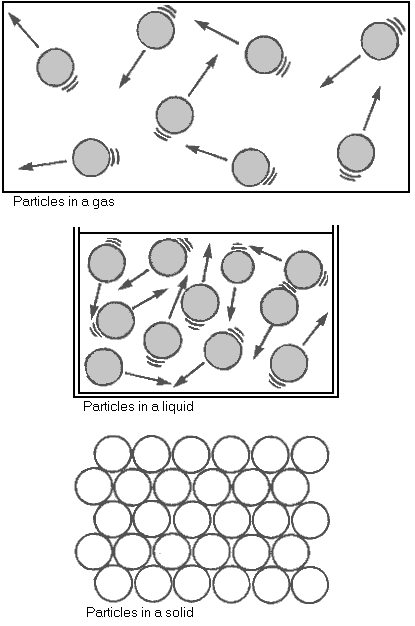
- Solid - Solids have a definite size and shape. Particles are close together, and vibrate.
- Liquid - Liquids do not have a fixed shape. Particles take the shape of their container. Particles are further apart, and can move freely.
- Gas - Gases do not have a fixed shape. Particles take the shape of their container. Particles are far apart, and move very freely.
CHANGES OF STATE
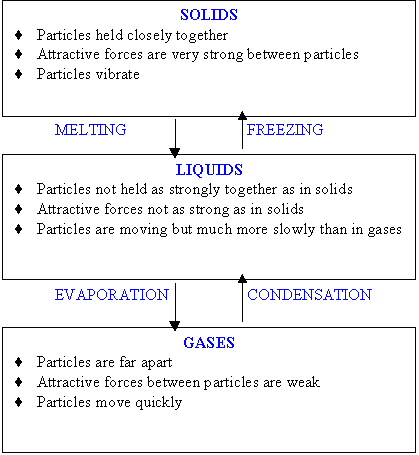
- Melting - the change of state from solid to liquid
- Freezing or Solidification - the change of state from liquid to solid
- Boiling or Evaporation - the change of state from liquid to gas
- Condensation - the change of state from gas to liquid
- Sublimation - the change of state directly from gas to solid, and vice versa (e.g. of carbon dioxide gas or carbon dioxide solid 'dry ice')
MELTING AND BOILING POINTS
- Melting Point - the temperature at which matter changes from solid to liquid, and vice versa (e.g. The melting point of water from ice to liquid water is 0oC.)
- Boiling Point - the temperature at which matter changes from a liquid to a gas, and vice versa (e.g. The boiling point of water from liquid water to steam is 100oC.)
CHEMICAL |
MELTING |
BOILING POINT |
STATE AT ROOM |
| Helium | -272 |
-269 |
gas |
| Hydrogen | -259 |
-252 |
gas |
| Oxygen | -218 |
-183 |
gas |
| Nitrogen | -210 |
-195 |
gas |
| Ethanol (Alcohol) | -114 |
79 |
liquid |
| Water | 0 |
100 |
liquid |
| Common Salt | 804 |
808 |
solid |
| Copper | 1083 |
2567 |
solid |
| Iron | 1535 |
2750 |
solid |
| Tungsten | 3410 |
5660 |
solid |